Discord Bot - Python: Difference between revisions
Created page with "== Preface == Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics. Its high-level built in data structures, combined with dynamic typing and dynamic binding, make it very attractive for Rapid Application Development, as well as for use as a scripting or glue language to connect existing components together. Python's simple, easy to learn syntax emphasizes readability and therefore reduces the cost of program maintenance. Pyt..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
Make sure the line starts with 'DISCORD_TOKEN=' like that. Then click 'Save Changes' and close the tab. Saving your token separate from your Python code is good practice because this way you can share the code on GitHub or something like that without worrying about people getting access to your bot. | Make sure the line starts with 'DISCORD_TOKEN=' like that. Then click 'Save Changes' and close the tab. Saving your token separate from your Python code is good practice because this way you can share the code on GitHub or something like that without worrying about people getting access to your bot. | ||
== Starting the Discord Bot == | |||
To start the Discord bot, read up on the rest of the guide at the [[:Discord_Bot#Starting_and_Stopping_Your_Bot|end of the Discord tutorial]]. | |||
[[Category:Tutorials]] | [[Category:Tutorials]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:53, 14 February 2026
Preface
Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics. Its high-level built in data structures, combined with dynamic typing and dynamic binding, make it very attractive for Rapid Application Development, as well as for use as a scripting or glue language to connect existing components together. Python's simple, easy to learn syntax emphasizes readability and therefore reduces the cost of program maintenance. Python supports modules and packages, which encourages program modularity and code reuse.
Write the Bot Script in Python
Log in and continue to Plesk. Then load up the file manager.
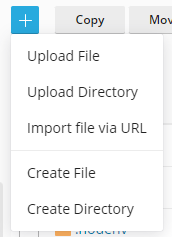
In the top left corner click the '+' plus sign, and select 'Create File'.
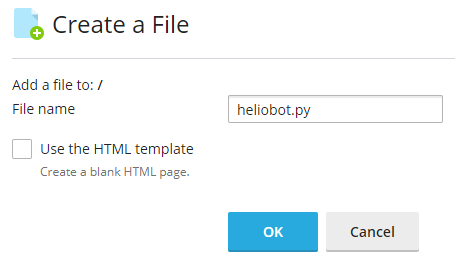
Then type the name of your new file: 'heliobot.py'.
You want to create this bot in your home directory so random hackers and bots on the internet can't access it directly. Make sure it says 'Add a file to: /' not 'Add a file to: /httpdocs' or any other folder.
Scroll down in the file manager and click on the new 'heliobot.py' file to edit it. Then copy/paste this code in:
#!/usr/bin/python3.12
import os
import discord
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
token = os.getenv('DISCORD_TOKEN')
import certifi
os.environ["SSL_CERT_FILE"] = certifi.where()
client = discord.Client(intents=discord.Intents.default())
class MyClient(discord.Client):
async def on_ready(self):
print(f'Logged in as {self.user} (ID: {self.user.id})')
print('------')
async def on_message(self, message):
# we do not want the bot to reply to itself
if message.author.id == self.user.id:
return
if message.content.startswith('!hello'):
await message.reply('Hello!', mention_author=True)
intents = discord.Intents.default()
intents.message_content = True
client = MyClient(intents=intents)
client.run(token)
The first line is called the shebang, and it tells the system which version of Python you want to use. Morty, Tommy, and Johnny also have Python 3.9, but we recommend using Python 3.12 like in the example.
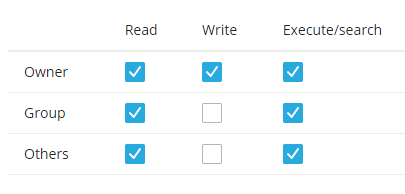
Once you have your code copy/pasted in click save in the bottom left corner. Now we need the bot to be executable so in the file manager click the 'rw- r-- r--' on the heliobot.py line.
Check all three of the 'Execute/Search' boxes so it looks like this and then click save in the bottom left corner.
Now we need to provide our Discord token to the bot so click the '+' plus sign, and select 'Create File' again and this time name the file '.env'.
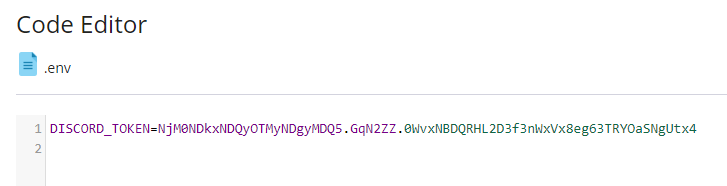
Make sure you start the filename with a period. It's easy to miss that in the screenshot. This file needs to be in the same directory as your Python script. Now you need to paste your Discord bot token into your '.env' file that you created. So go back to the Plesk file manager and click the '.env' file to edit it. Paste the token into the file like this:
Make sure the line starts with 'DISCORD_TOKEN=' like that. Then click 'Save Changes' and close the tab. Saving your token separate from your Python code is good practice because this way you can share the code on GitHub or something like that without worrying about people getting access to your bot.
Starting the Discord Bot
To start the Discord bot, read up on the rest of the guide at the end of the Discord tutorial.