Flask: Difference between revisions
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | ||
|+ Tommy server | |+ style="caption-side:top; |'''Tommy server''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Server !! Flask Version !! Python Version !! Python Modules Installed !! Python Path !! Loader | ! Server !! Flask Version !! Python Version !! Python Modules Installed !! Python Path !! Loader | ||
Revision as of 02:06, 26 October 2024
Flask
About Flask
Flask is a Python web framework built with a small core and easy-to-extend philosophy. Read more at Full Stack Python.
Johnny server

If you need to run Flask on another version of Python, you'll need to get a VPS. You can get a 10% discount when you pay for 6 months upfront.
| Server | Flask Version | Python Version | Python Modules Installed | Python Path | Loader |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johnny | 3.0.3 | 3.12 | View | /usr/bin/python3.12 | WSGI |
Tommy server

If you need to run Flask on another version of Python, you'll need to get a VPS. You can get a 10% discount when you pay for 6 months upfront.
| Server | Flask Version | Python Version | Python Modules Installed | Python Path | Loader |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tommy | 5.0.7 | 3.12 | View | /usr/bin/python3.12 | WSGI |
How To Setup Flask on Plesk
Create a directory on your main domain called `flasktest`.
If you were transferred from the old cPanel, your main domain will be parked on the `public_html` directory.
If you created a new account on Plesk, your directory will be `httpdocs`.
Create an `.htaccess` file inside the `flasktest` directory with these contents:
Options +ExecCGI RewriteEngine On RewriteBase / RewriteRule ^(media/.*)$ - [L] RewriteRule ^(admin_media/.*)$ - [L] RewriteRule ^(flask\.wsgi/.*)$ - [L] RewriteRule ^(.*)$ flasktest/flask.wsgi/$1 [QSA,PT,L]
Create a file named `flask.wsgi` inside the `flasktest` directory with these contents:
import os, sys
# edit your path below
sys.path.append("/home/domain.helioho.st/httpdocs/flasktest");
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(__file__))
from myapp import app as application
# set this to something harder to guess
application.secret_key = 'secret'
Create a file named `myapp.py` inside the `flasktest` directory with these contents:
import sys
from flask import Flask, __version__
app = Flask(__name__)
application = app
@app.route("/")
def hello():
return """
Flask is working on HelioHost.<br><br>
<a href="/flasktest/python/version/">Python version</a><br>
<a href="/flasktest/flask/version/">Flask version</a>
"""
@app.route("/python/version/")
def p_version():
return "Python version %s<br><br><a href='/flasktest/'>back</a>" % sys.version
@app.route("/flask/version/")
def f_version():
return "Flask version %s<br><br><a href='/flasktest/'>back</a>" % __version__
if __name__ = "__main__":
app.run()
Make sure your directory structure and files look like this:
flasktest/ ├── flask.wsgi ├── .htaccess └── myapp.py 0 directories, 3 files
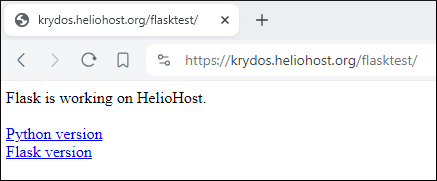
If you did everything right it should look like the below:
Screenshot taken from https://krydos.heliohost.org/flasktest/
WSGI Uses Caching

Flask changes can take up to 2 hours to appear consistently on your site because WSGI uses server side caching.
If you want site changes to take effect immediately, we offer a few options to work around caching.
What Caching Does
Multiple Apache processes are running on the server, and each time you refresh your site you are randomly assigned to one of these processes. If that particular process has already displayed your site, it shows the cached version of your code; otherwise, it shows the new code changes. This means that during the first 2 hours after a site change, you may intermittently see old or new content, depending on which process you get assigned to. This situation will resolve when Apache is restarted, which happens every 2 hours.
Options to Work Around Caching
Request WSGI Control Access
A new feature currently in beta is the ability for users to restart their Flask app themselves.
To request this, please create a new post in the Customer Service forum and provide your username, server name, and the domain name(s) you want to be given WSGI Control Access for. (If you have 2 Flask apps on 2 different domains, you need to request WSGI Control Access for each domain.)
Once you have been given WSGI Control Access, you can edit your `flask.wsgi` to reload your Flask app so new code changes load immediately. The edits to the file can be as simple as adding or removing a space or a blank line. As long as the file's `last modified date` changes it will discard the cache and reload your Flask app.
Please let us know if you experience unexpected results with this new feature.
Account Resets Remove WSGI Control Access

If you request an account reset you will need to re-request WSGI Control Access after the reset has been completed. By default, account resets will disable WSGI Control Access.
Use Local Development Environment
Another option to see code changes reflected immediately is to develop your Flask app on your home computer and then host the production copy on the server.
VPS
You may prefer to explore one of our paid VPS plans, depending on your requirements. You can get a 10% discount when you pay for 6 months upfront.
Troubleshooting
If you receive an error of `You don't have permission to access /flasktest/flask.wsgi/ on this server`, you may need to add `AddHandler cgi-script .py` on a new line in your `.htaccess` file.
Running Flask at the Webroot
The above example is for Flask in a subdirectory, so users can host different projects in different subdirectories rather than dedicating the whole domain to one Flask app.
If you prefer to run Flask at the webroot instead, this is possible with some slight changes to the `.htaccess`, `flask.wsgi`, and `myapp.py` files.
References
This tutorial is adapted from the How to Use Flask on Plesk post on the HelioNet forum, answered by Krydos.