Discord Bot - Rust: Difference between revisions
Created page with "== Preface == Rust is a compiled, strongly and statically typed general purpose programming language. Compared to Python, Rust applications must be compiled for each operating system and architecture combination, and all variables defined should have a single type. To learn more about Rust, read [https://doc.rust-lang.org/book/ "The Book"], or follow a more [https://doc.rust-lang.org/rust-by-example/ interactive learning guide] with example code and output. == Getting..." |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
To get started, install Rust and Cargo (the package manager for Rust) using [https://rustup.rs/ rustup]. | To get started, install Rust and Cargo (the package manager for Rust) using [https://rustup.rs/ rustup]. | ||
Once installed, create a new project by using < | Once installed, create a new project by using Cargo. | ||
<pre> | |||
cargo init ping-pong-rs | |||
</pre> | |||
Running <code>cargo init ping-pong-rs</code> will create a folder named <code>ping-pong-rs</code> with the basic structure of a Rust project. | Running <code>cargo init ping-pong-rs</code> will create a folder named <code>ping-pong-rs</code> with the basic structure of a Rust project. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 23: | ||
Next, we need to install some dependencies (crates). For this tutorial, we'll be using [https://crates.io/crates/serenity serenity] to interact with Discord, [https://crates.io/crates/tokio tokio] with the "full" feature to manage asynchronous behavior, and [https://crates.io/crates/dotenvy dotenvy] to read your Discord bot token from a file. | Next, we need to install some dependencies (crates). For this tutorial, we'll be using [https://crates.io/crates/serenity serenity] to interact with Discord, [https://crates.io/crates/tokio tokio] with the "full" feature to manage asynchronous behavior, and [https://crates.io/crates/dotenvy dotenvy] to read your Discord bot token from a file. | ||
To install these crates, use < | To install these crates, use need to use Cargo again. | ||
<pre> | |||
cargo add dotenvy tokio serenity -F tokio/full | |||
</pre> | |||
Once you have the crates installed, you are now ready to code! | |||
== Writing the Discord Bot == | == Writing the Discord Bot == | ||
| Line 86: | Line 93: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Finally, you are now ready to run your bot locally to test it out! | Finally, you are now ready to run your bot locally to test it out! | ||
<pre> | |||
cargo run | |||
</pre> | |||
The run command will build and run your bot locally. Remember, Rust is a compiled language. This means that your bot must be compiled before it can be run, this can take around a minute. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
lucas@fozziebear:~/heliohost/ping-pong-rs$ cargo run | lucas@fozziebear:~/heliohost/ping-pong-rs$ cargo run | ||
| Line 113: | Line 124: | ||
Rust applications must be built to run on the machine that you want to run your application on. In simple terms, this means that to run a Rust Discord bot on HelioHost, you should build a Linux x86_64 application. | Rust applications must be built to run on the machine that you want to run your application on. In simple terms, this means that to run a Rust Discord bot on HelioHost, you should build a Linux x86_64 application. | ||
For users that are writing code on a Windows machine (this does not include WSL2), or a MacOS machine, you will need to cross compile to the correct architecture. | |||
=== Building a release binary on the same architecture and host === | |||
If you are on a system that '''matches''' the HelioHost machines (Linux x86_64), then you do not need to cross compile. Simply running a normal release build is enough. | |||
<pre>cargo build --release</pre> | |||
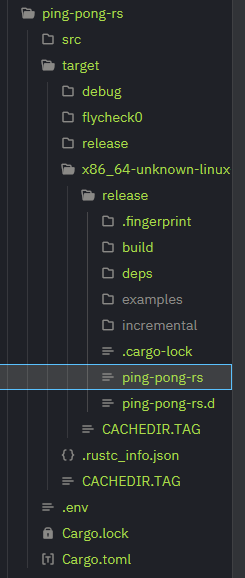
This will build the final file under <code>target/release/ping-pong-rs</code>. | |||
[[File:Rust_discord_build_cargo.png]] | |||
=== Building a release binary on a different host === | |||
If you are on a system that '''does not match''' the HelioHost machines (Linux x86_64), then you do not need to cross compile. This includes Windows, MacOS, or Linux ARM machines. | |||
The most straightforward way to do this is by using [https://github.com/cross-rs/cross cross] to build your application inside of a Docker container. | |||
To get started, install [https://www.docker.com/ Docker]. This is most commonly done by installing Docker Desktop for those using Windows or MacOS. | |||
Once you have Docker installed and running, install cross by using Cargo. | |||
<pre> | |||
cargo install cross --git https://github.com/cross-rs/cross | |||
</pre> | |||
After cross has completed building and installing, create a release build for the Linux x86_64 architecture using the tool. | |||
<pre> | |||
cross build --target x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu --release | |||
</pre> | |||
This will build the final file under <code>target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/ping-pong-rs</code>. | |||
[[File:Rust_discord_build_cross.png]] | |||
== Upload Files to Plesk == | |||
You will need to upload both your environment variable file and the binary to your Plesk account to setup. | |||
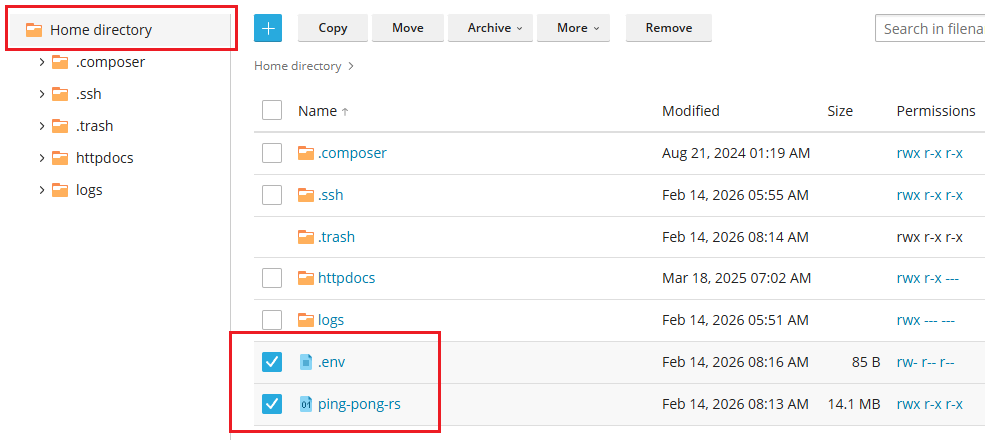
Navigate to your '''Home Directory''' and upload both the <code>.env</code> and <code>ping-pong-rs</code> files. | |||
[[File:Rust_upload_plesk.png]] | |||
== Starting the Discord Bot == | |||
To start the Discord bot, read up on the rest of the guide at the [[:Discord_Bot#Starting_and_Stopping_Your_Bot|end of the Discord tutorial]]. | |||
[[Category:Tutorials]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:10, 14 February 2026
Preface
Rust is a compiled, strongly and statically typed general purpose programming language. Compared to Python, Rust applications must be compiled for each operating system and architecture combination, and all variables defined should have a single type.
To learn more about Rust, read "The Book", or follow a more interactive learning guide with example code and output.
Getting Started
What to expect in this section:
- Installing Rust and Cargo
- Setting up a Rust project
- Installing needed dependencies (also known as "crates")
To get started, install Rust and Cargo (the package manager for Rust) using rustup.
Once installed, create a new project by using Cargo.
cargo init ping-pong-rs
Running cargo init ping-pong-rs will create a folder named ping-pong-rs with the basic structure of a Rust project.
Next, we need to install some dependencies (crates). For this tutorial, we'll be using serenity to interact with Discord, tokio with the "full" feature to manage asynchronous behavior, and dotenvy to read your Discord bot token from a file.
To install these crates, use need to use Cargo again.
cargo add dotenvy tokio serenity -F tokio/full
Once you have the crates installed, you are now ready to code!
Writing the Discord Bot
What to expect in this section:
- Creating an example ping-pong bot
- Building and testing your Discord bot on your machine
We'll be using a modified version of serenity's sample ping-pong bot. Open the main.rs file located in the src folder and paste the following code inside of it:
use std::env;
use dotenvy::dotenv;
use serenity::async_trait;
use serenity::model::channel::Message;
use serenity::prelude::*;
struct Handler;
#[async_trait]
impl EventHandler for Handler {
async fn message(&self, ctx: Context, msg: Message) {
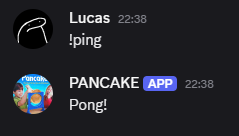
if msg.content == "!ping" {
if let Err(why) = msg.channel_id.say(&ctx.http, "Pong!").await {
println!("Error sending message: {why:?}");
}
}
}
}
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
// Load all variables from a local environment variable file
dotenv().expect("Expected a .env file to be created");
// Login with a bot token from the environment
let token = env::var("DISCORD_TOKEN").expect("Expected a token in the environment");
// Set gateway intents, which decides what events the bot will be notified about
let intents = GatewayIntents::GUILD_MESSAGES
| GatewayIntents::DIRECT_MESSAGES
| GatewayIntents::MESSAGE_CONTENT;
// Create a new instance of the Client, logging in as a bot.
let mut client = Client::builder(&token, intents)
.event_handler(Handler)
.await
.expect("Err creating client");
println!("Starting bot");
// Start listening for events by starting a single shard
if let Err(why) = client.start().await {
println!("Client error: {why:?}");
}
}
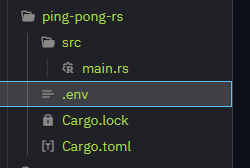
Next, you'll need to copy your Discord bot token into a file named .env. This file should be located in the same place as the src folder, NOT inside of it.
The environment file should contain your token:
DISCORD_TOKEN=your_discord_bot_token
Finally, you are now ready to run your bot locally to test it out!
cargo run
The run command will build and run your bot locally. Remember, Rust is a compiled language. This means that your bot must be compiled before it can be run, this can take around a minute.
lucas@fozziebear:~/heliohost/ping-pong-rs$ cargo run
Compiling proc-macro2 v1.0.106
Compiling quote v1.0.44
.
.
.
Compiling hyper-rustls v0.27.7
Compiling reqwest v0.12.28
Compiling ping-pong-rs v0.1.0 (/home/lucas/heliohost/ping-pong-rs)
Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 41.00s
Running `target/debug/ping-pong-rs`
Starting bot
You should see the message Starting bot at the end if everything compiled successfully.
Once your project is up and running, return to Discord and type !ping in the channel your bot is located in and see it return your message!
Building your Discord Bot for HelioHost
What to expect in this section:
- How to build the correct file to work in HelioHost
Rust applications must be built to run on the machine that you want to run your application on. In simple terms, this means that to run a Rust Discord bot on HelioHost, you should build a Linux x86_64 application.
For users that are writing code on a Windows machine (this does not include WSL2), or a MacOS machine, you will need to cross compile to the correct architecture.
Building a release binary on the same architecture and host
If you are on a system that matches the HelioHost machines (Linux x86_64), then you do not need to cross compile. Simply running a normal release build is enough.
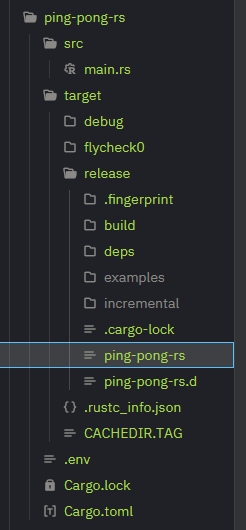
cargo build --release
This will build the final file under target/release/ping-pong-rs.
Building a release binary on a different host
If you are on a system that does not match the HelioHost machines (Linux x86_64), then you do not need to cross compile. This includes Windows, MacOS, or Linux ARM machines.
The most straightforward way to do this is by using cross to build your application inside of a Docker container.
To get started, install Docker. This is most commonly done by installing Docker Desktop for those using Windows or MacOS.
Once you have Docker installed and running, install cross by using Cargo.
cargo install cross --git https://github.com/cross-rs/cross
After cross has completed building and installing, create a release build for the Linux x86_64 architecture using the tool.
cross build --target x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu --release
This will build the final file under target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/ping-pong-rs.
Upload Files to Plesk
You will need to upload both your environment variable file and the binary to your Plesk account to setup.
Navigate to your Home Directory and upload both the .env and ping-pong-rs files.
Starting the Discord Bot
To start the Discord bot, read up on the rest of the guide at the end of the Discord tutorial.